PCOS or Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is becoming more prevalent amongst women who are in their menstruating or reproductive age. However, its complications last even after menopause. The causes of this disorder could be a combination of genetic or environmental factors. Doctors also believe that this could be caused due to high level production of the male hormones such as Testosterone and Androgen in women.
How do you know if you’re diagnosed with PCOS?
The symptoms often develop during puberty when a girl starts menstruating or later in response to weight gain.
Irregular Periods
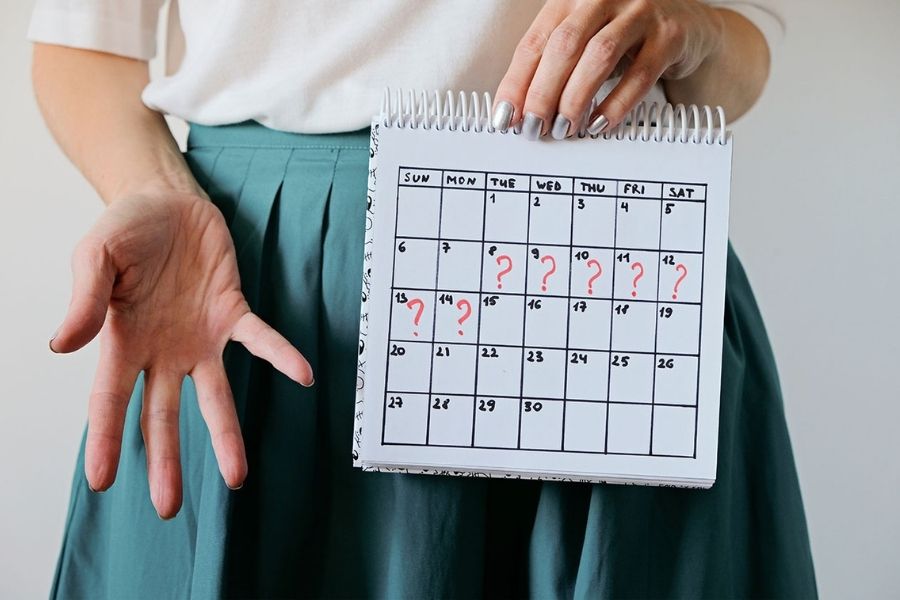

This is the most common symptom of PCOS. It includes prolonged or irregular menstrual cycles wherein you may experience less than 9 periods a year or extremely heavy periods.
Excess Androgen
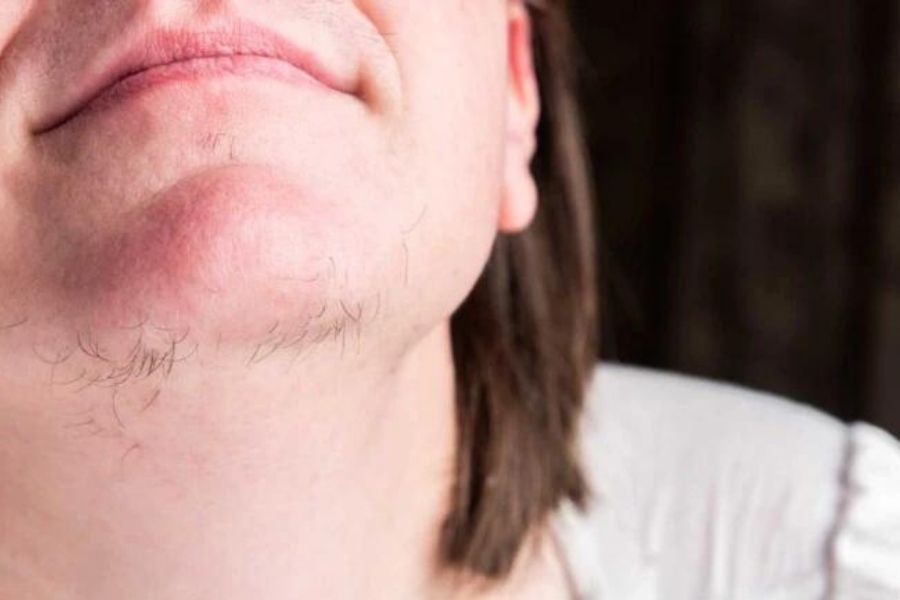
Women suffering from PCOS are likely to produce an abnormal amount of androgens that may result in physical signs. This includes Hirsutism (facial or body hair), male pattern baldness, acne and other skin conditions.
Polycystic Ovaries

This causes enlarged eggs that grow follicles around them, restricting them from functioning regularly.
What are the causes?
Heredity

Genetic factors have been severely linked to PCOS. If a line of women in your family have seen the pattern of getting diagnosed with PCOS, it is no surprise that it has come down to you too.
Excess Insulin & Androgen

The production of these hormones go hand in hand. Excess production of insulin links to excess production of androgen that can raise your blood sugar levels and make you vulnerable to this condition.
Dairy Products

The dairy products come from cattle that was injected with hormones to produce more amounts of milk. Consumption of this milk can also affect your hormone levels.
What Complications will you go through?
Infertility
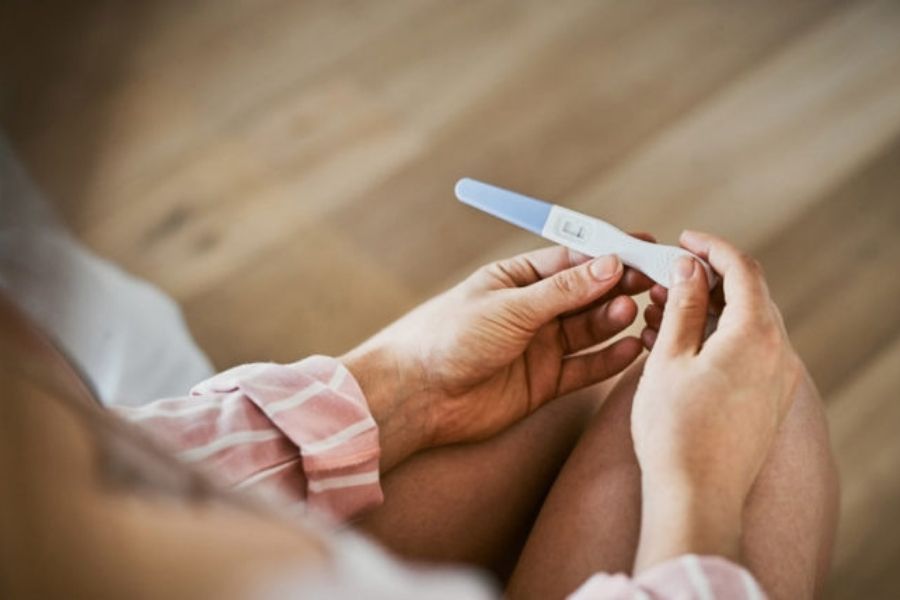

If diagnosed with PCOS, it reduces your chance of getting pregnant naturally. Nevertheless, you can opt for IVF (In Vitro Fertilization).
Miscarriage or Premature Birth

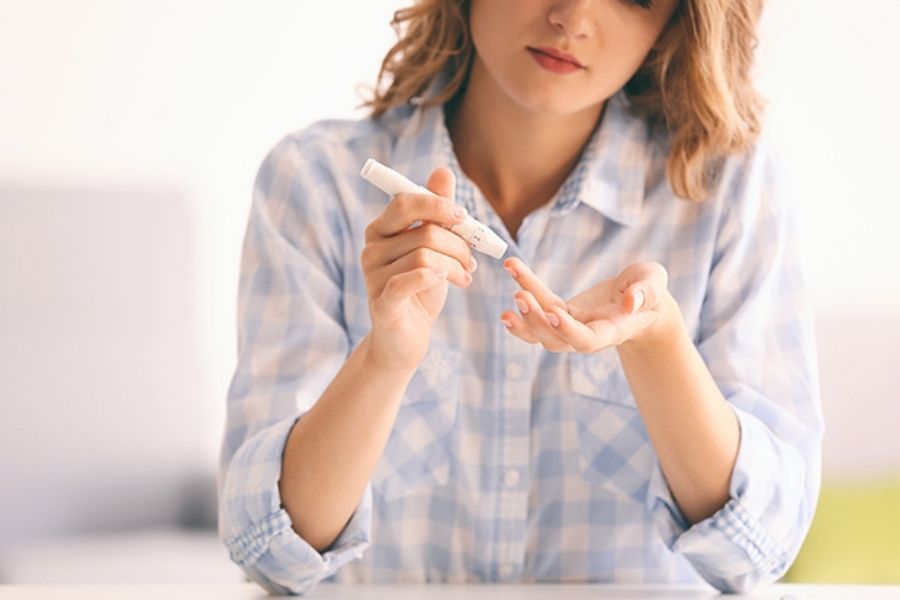
Diabetes

Depression, Eating Disorders or Anxiety

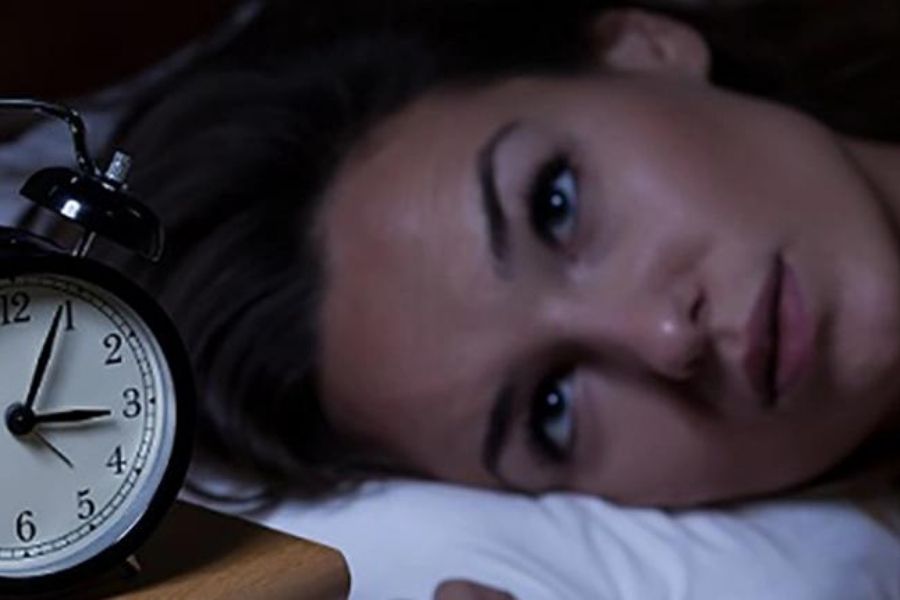
Insomnia

Endometrial Cancer

Liver Inflammation

Uterine Bleeding

High Cholesterol Levels

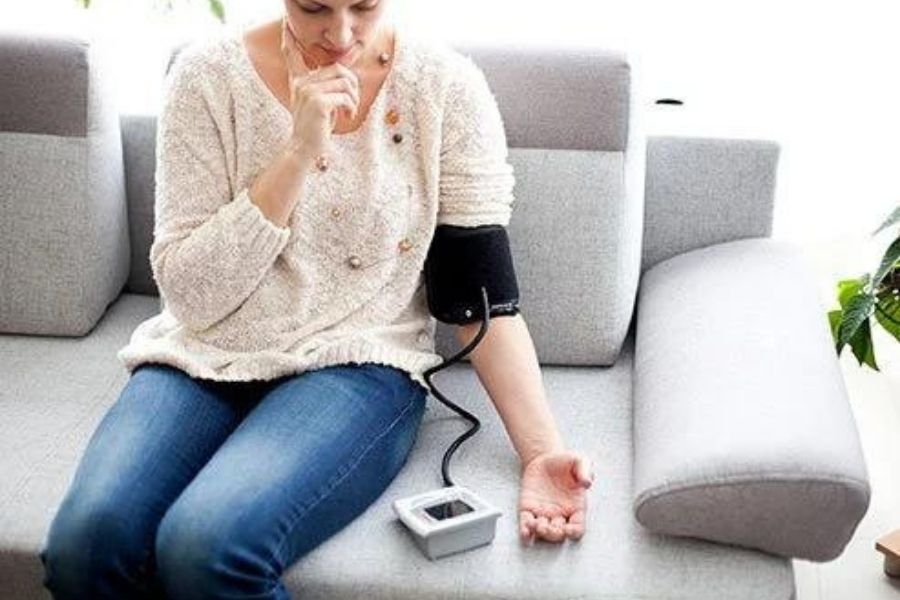
High Blood Pressure

Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases

Is there a Treatment?

There is no cure for PCOS but its symptoms can be controlled with the help of medication that includes birth control pills, hormonal injections or pills of estrogen etc. However, a majority of women prefer a more natural approach. This can be achieved through some healthy lifestyle changes such as:
Regular Exercise

Exercising daily for 30 minutes can help one lose weight. This can be useful for regulating abnormal symptoms.
Good Eating Habits

Cutting down on food items such as dairy products, refined carbohydrates, sugary items such as cakes, canned juices, breads and muffins or anything that can spike your insulin levels can help you maintain your blood sugar and hormone levels.
Good Sleep
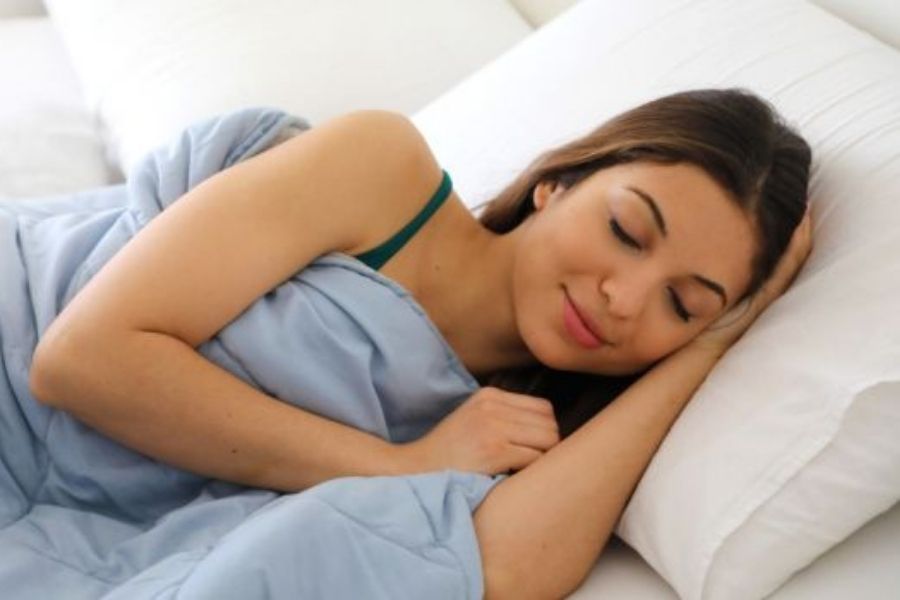

It is necessary to get good eight hours of sleep every day.
In the end, it is important for any woman diagnosed with PCOS to realize that she is not any different from others around her. It is alright to be diagnosed with this condition, but never stop working hard to reach your absolute best self. PCOS does not make you any less of a woman.







