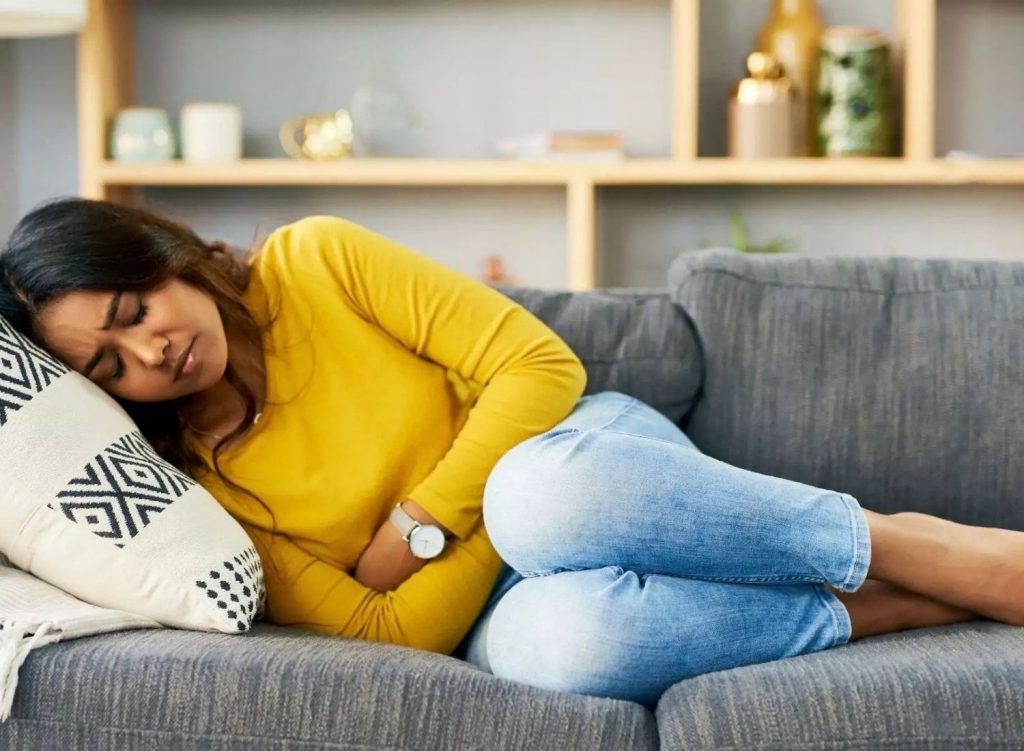
Irritable bowel syndrome is a health disorder that affects the large intestine. One study stated that your colon gets oversensitive and start overreacting to mild stimulation. Instead of slow muscle movements, the bowel muscles begin to spasm, causing either diarrhea or constipation. The second study stated that IBS happens when the bowels’ muscles don’t usually squeeze, affecting stool movement. But reviews don’t seem to back this up. A theory suggests that certain chemicals like serotonin and gastrin control nerve signals between the brain and digestive tract. Genetics is suggested as a potential cause of IBS.
The physical processes involved in IBS consist of:
- An abnormal serotonin levels in the colon
- Celiac disease damages the intestines
- Spastic movements of the colon, causing cramping
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Triggers
Depression, anxiety, or certain foods can be the triggers for many people with IBS. It is better to keep a food diary for a period to learn which foods are responsible. Such things may increase your levels of stress and anxiety can help. It can give you time to either plan to avoid these situations when possible or develop strategies to limit the stress and anxiety. Stress can affect your nerves, making your digestive system overactive.
Note: IBS is not the same as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a more serious condition that causes inflammation in the digestive tract and can result in complications.
Risk Factors For Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)

- Sex: IBS is quite common among women than men.
- Age: Age factor wise IBS occurs more frequently in people under age 50.
- Hereditary: Genes may play a role, as they may share factors in a family’s environment or a combination of genes and environment.
- Stress factors: Stressors (anxiety, depression, or other mental health issues) are associated with IBS.
Other Important Factors Responsible For IBS
- An infection of the stomach and intestines caused by a virus or bacteria
- Hypersensitivity to pain caused by gas
- Abnormal movements of the colon
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
- Reproductive hormones may be off-balance in people with IBS
Complications Of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Chronic constipation or diarrhea can cause hemorrhoids. Additionally, IBS is associated with:
- Poor quality of life: Research indicates that people with IBS miss three times as many days from work as do those without bowel symptoms.
- Mood disorders: IBS can lead to depression or anxiety.
How Is Irritable Bowel Syndrome Diagnosed?

IBS is called a diagnosis of exclusion, which means a physician considers many other alternatives and performs tests to rule out other medical problems. An endoscopy is a technique in which a flexible tube with a micro-camera at one end is passed into the GI tract while the patient is in a conscious state. A combination of history, physical examinations, and some critical selected tests helps diagnose irritable bowel syndrome.
Tests To Be Done If You Have IBS
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy to look for signs of blockage or inflammation in your intestines
- Upper endoscopy if you have heartburn or indigestion
- X-rays
- Stool tests for blood or infections
- Blood tests
- Tests for lactose intolerance, gluten allergy, or celiac disease
Treatments For Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Both the physician and the patient will need to work together to find the right treatment plan to manage your symptoms. New blood antibody blood tests may help doctors diagnose irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea or IBS-D. These new blood tests are for anti-cdtB and anti-vinculin antibodies, which researchers believe, are thought to develop in some patients after acute gastroenteritis. They also help doctors to differentiate between conditions like IBS and IBD (inflammatory bowel disease).
Home Remedies To Treat Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)

- Avoid taking certain foods that “trigger” or worsen diarrhea, bloating, and gas, such as cruciferous vegetables like wasabi, cauliflower, kale, broccoli, black beans, soy nuts, etc.
- If you’re lactose intolerant, try substituting yogurt or take Greek yogurt for milk.
- Consuming small amounts of milk products at a time also may help.
- Add fiber to the diet, drink plenty of water, avoid soda and caffeinated beverages, and eat fewer or smaller meals.
- Do 30 mins of exercise regularly, like walking, jogging, yoga, etc. It helps relieve depression and stress and stimulates normal contractions of your intestines.
- Medical treatment for irritable bowel syndrome includes anti-spasmodic medicines, anti-diarrheal medicines, anti-depressants, laxatives, etc., that need to be taken under the doctor’s observation.
Prevention Of IBS
A counselor can help you learn to modify or change your responses to stress. Studies have shown that psychotherapy can provide significantly. The stress-reduction technique helps you focus on being in the moment and letting go of worries and distractions. The electrical sensors help you receive information (feedback) on your body’s functions, focusing on making subtle changes, such as relaxing specific muscles, to ease symptoms. Progressive relaxation exercises help you relax muscles in your body, one by one.







