Obesity is spreading worldwide and its increasing prevalence of conditions associated with a large number of comorbid diseases like stroke cardiovascular diseases and TP2DM. Among these, the most common is obesity-induced hypertension. Obesity, particularly central obesity, is consistently associated with hypertension and increased cardiovascular risk.
What Is Blood Pressure?
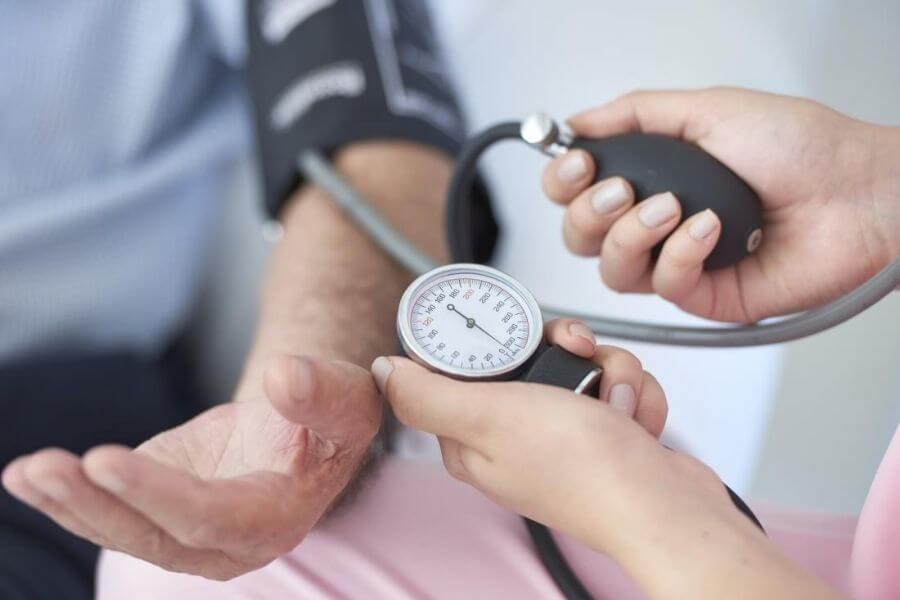

Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by blood on the walls of arteries as the heart pumps. We all need normal blood pressure to push blood through the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and organs.
Blood pressure consists of two values. Normal blood pressure is noted by 120/80 mm of Hg, where 120 represents SBP and 80 DBP. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) is the pressure in the blood vessels when the heart contract for pumping blood. Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) is the pressure in the blood vessels when the heart relaxes in between beats.
What Is High Blood Pressure?

High blood pressure is also known as arterial hypertension. It means that your SBP is equal to or greater than 140 mm of Hg and DBP equal to or greater than 90 mm of Hg.
Causes of Hypertension
There are many potential causes of hypertension. But here we will see hypertension caused due to genetic factors and faulty lifestyle.
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Stress and emotional burdens
- Excessive consumption of salt and salted food items
- Consumption of fats and fatty food items
So we are going to discuss mainly obesity and how it actually causes hypertension.
What Is Obesity?

Obesity is a complex disorder in which the body accumulates excess fat in different areas. It causes adverse health effects, leading to an increase in disease incidence and causes a decrease in life expectancy.
Types Of Obesity
There are two types of obesity according to fat distribution in the body.
- Peripheral obesity or gynoid obesity (pear-shaped body)
- Abdominal obesity or android obesity (apple-shaped body)
Peripheral obesity is characterized by the accumulation of subcutaneous fat, mainly in thighs, hips, and buttocks. This kind of fat is found just underneath the skin.
Abdominal obesity is characterized by the accumulation of visceral fat, mainly found in the abdominal cavity around the viscera. This kind of fat is found situated deep inside the skin. It is also called as central obesity, which is considered amongst the main culprit of “metabolic syndrome.”
How Obesity-induced Hypertension Is Caused?

Both types of obesity affect blood pressure in the following way. This is a proposed or claimed way of how obesity-induced hypertension is caused.
- Excessive subcutaneous fat forms inflammatory kinins, and they inflame the lining of the arteries.
- Fatty substances like triglycerides and LDL cholesterol are circulating freely in a blood vessel. They get deposited in the form of “macrophages’ and turn into foam cells. Foam cells attack the lining of arteries. Arteries start narrowing, which makes it harder to pump blood efficiently.
- The kidneys have specific cells that measure blood supply to the kidney’s blood vessels. When blood flow is deteriorated due to excessive fat deposited, renin is released from the cells, which elevates blood pressure.
- Visceral fat is a fat that wraps vital organs like kidneys, pancreas, liver, small intestine, etc. This fat ensures the proper distance between each organ. Too much visceral fat leads to compression of organs obstructing the normal functioning capacity of these organs.
- Also, visceral fat interacts intimately with the function of kidneys and adrenal glands, which are responsible for regulating blood pressure. Thus, it interferes with the function of the organs; visceral fat is a serious promoter of high blood pressure. This leads to obesity-induced hypertension.
Tools For Calculating Obesity And Visceral fat
There are a few ways that can help us to calculate obesity and visceral fat in our body. The most commonly used tool for knowing it is BMI. Given below are a few more ways you can use.
1. Body Mass Index (BMI)
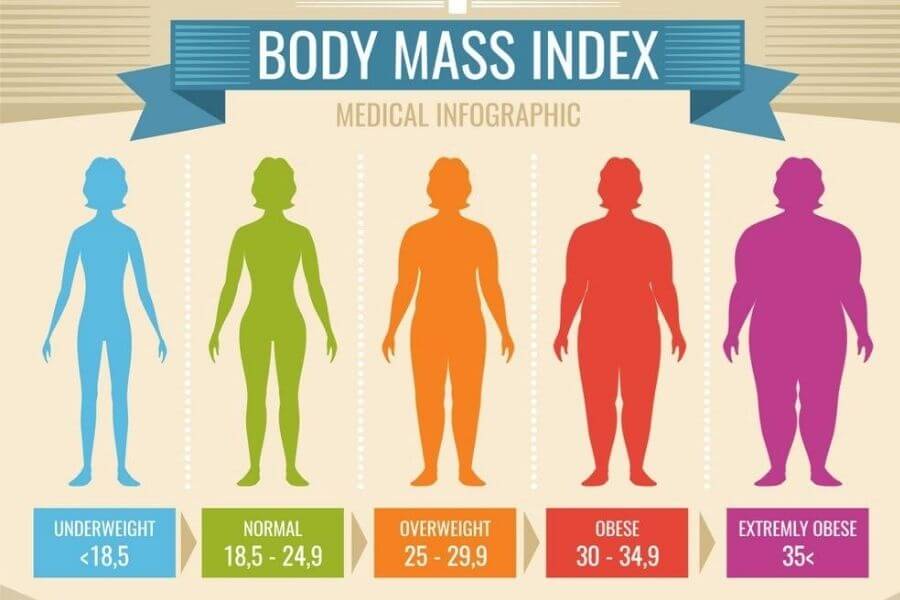
It is the ratio of the present weight and height of the person. In the above pic, it is shown that person with BMI ranges between 25 – 35 and above 35 is considered at risk of hypertension.
2. Waist Circumference
Waist circumference above 35 inches in women and above 40 inches in men is an indicator of visceral fat deposition, which is considered as a risk for hypertension and many other diseases. This is an easy method and inexpensive.
3. Waist To Hip Ratio (WH Ratio)
Waist hip ratio is measured by taking the ratio of the circumference of waist and hip. WH ratio greater than 0.8 in women and 0.9 in men is considered at risk. It is used to measure abdominal obesity.
4. Body Composition Analysis (BCA)
It is commonly used in gyms and is a good source of knowing your body composition. It gives a gross idea of all parameters, fat percentage, and visceral fat. It is calculated by passing a small bioelectrical impedance from your body. It is a painless procedure.
5. MRI And CT Scanning
MRI and CT Scanning is expensive but gives an accurate value of visceral fat underlying. It helps in evaluating the abdominal fat consumption.








Surly this article will help to all people