The above question or statement is a little tricky and vast to say in one line.
Cloning does not only signify making copies of humans – it helps us to fight various diseases as well. But is it right to fight with mother nature? And what about the accidental results of cloning?
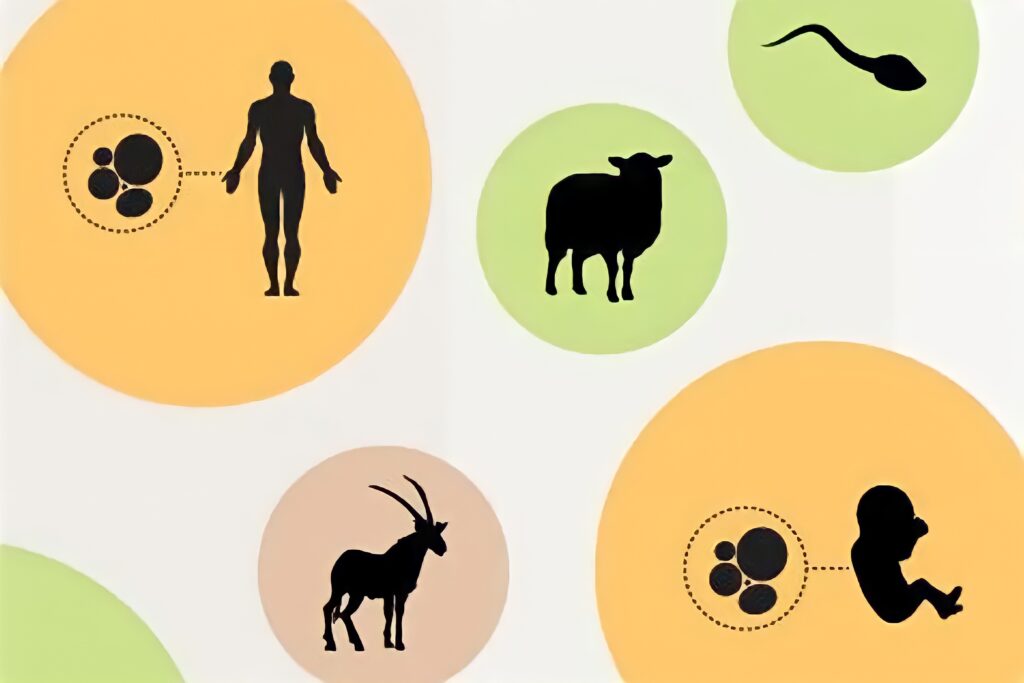

The whole process is vast and quite complicated. Cloning is a technique used by scientists to make exact genetic copies of living beings. Genes, tissues, and even animals can all be cloned. Did you know that single-celled organisms such as bacteria make copies of themselves each time they reproduce? In human biology, identical twins are created when a fertilized ova splits in two. Identical twins are quite similar to clones; they share the same genes.
Scientists make clones in their authorized laboratory. They clone genes to research and study and for a better understanding of them. For the cloning of a gene, researchers extract DNA from a living creature and place it into a carrier like bacteria, etc.
Every time that carrier reproduces, a new copy of the gene is created. Today, cloning is quite an advanced area of scientific research with its better potential to treat human diseases. An animal, that is a clone, is an exact copy of the animal that donated its DNA for its creation.

Have you heard about Therapeutic Cloning?
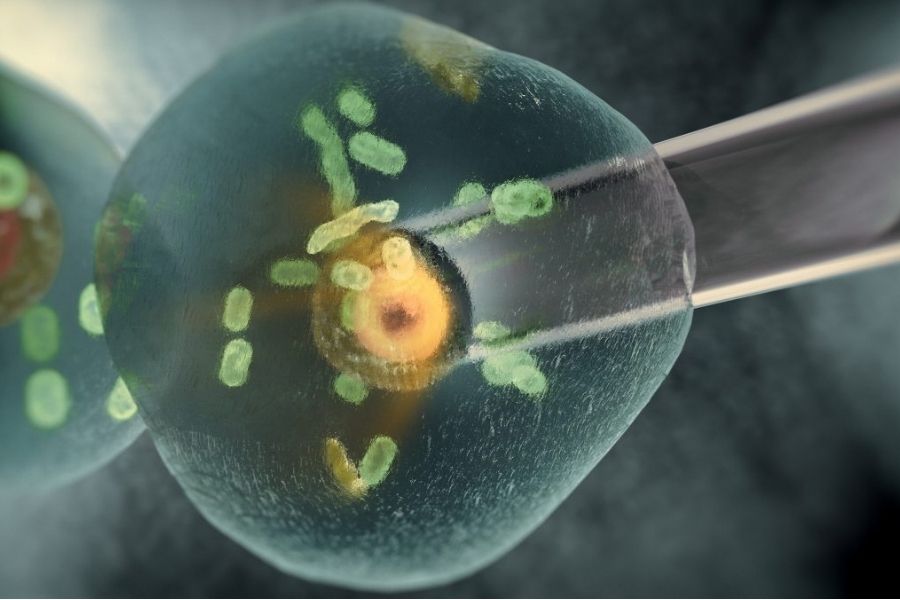
Therapeutic cloning is the combining of the body of an egg cell with the nucleus of another cell from another place in that organism.
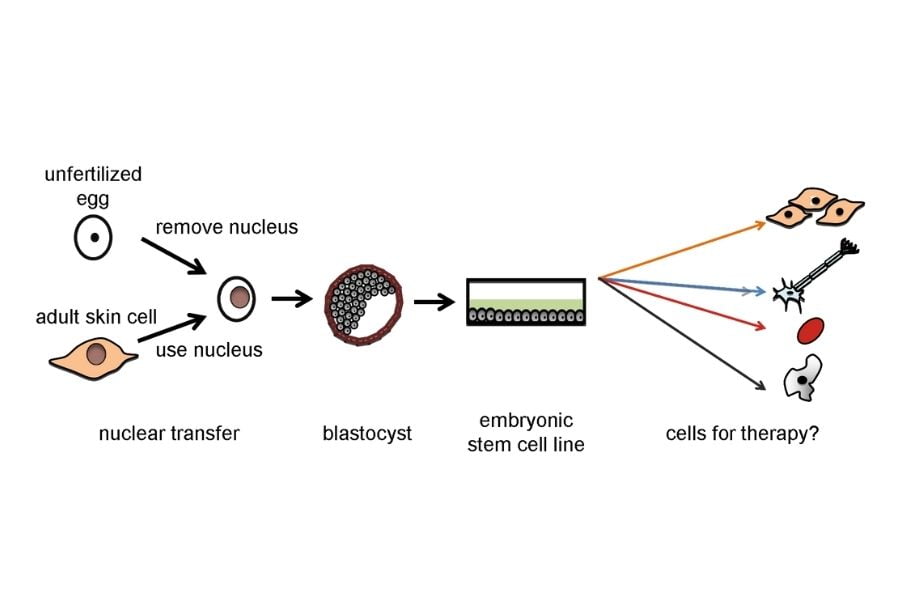
When these parts of the two cells are fused, they make stem cells. It’s safe to say that therapeutic cloning can save a lot of lives. Not only that – in the future, cloning technology could entirely change the way we think about curing different types of diseases.
There are a lot of questions that come with this scientific invention and just because we can do something doesn’t mean we should, but there’s a huge amount of work, theses, and research going on to make treatments based on therapeutic cloning as well as stem cells:
Spinal Cord Injuries
Early experiments have shown that stem cell treatments might be able to repair damaged or injured spinal cords.
Degenerative Brain Diseases
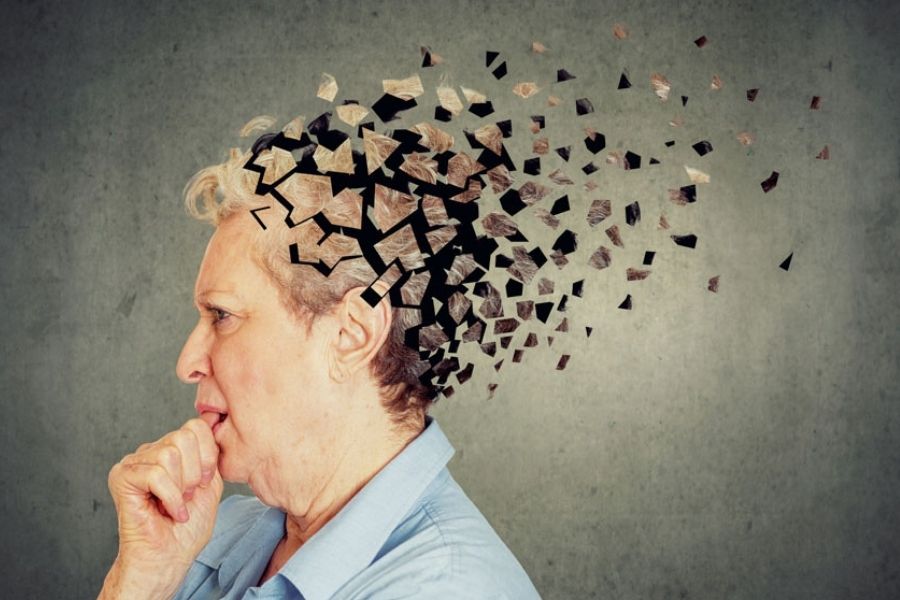

Stem cell therapy might cure or reduce conditions like Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s.
Heart Diseases

Unlike other muscles, the heart can’t repair itself if it gets damaged. So, scientists have begun to work out how stem cells could be used to repair hearts.
Teeth

Scientists can use stem cells to grow an entire set of teeth in the laboratory. They’re now working on it for more authenticity.
HIV/Aids
This virus destroys the immune system. Scientists have recently started researching and experimenting with the use of stem cells to repair the human immune system.
We all know that cells contain DNA and to make a clone, DNA is removed from one of its cells. This DNA is then placed in an egg cell of a female animal. The cloned egg is then placed in the female animal’s uterus to grow and develop. This is a quite complex procedure but experiments are going on for further proof.
It has been shown in researches and experiments that most clone animals die pre-birth. It has also been noted that post-birth cloned animals face more health issues than average ones as well as a shorter life expectancy.
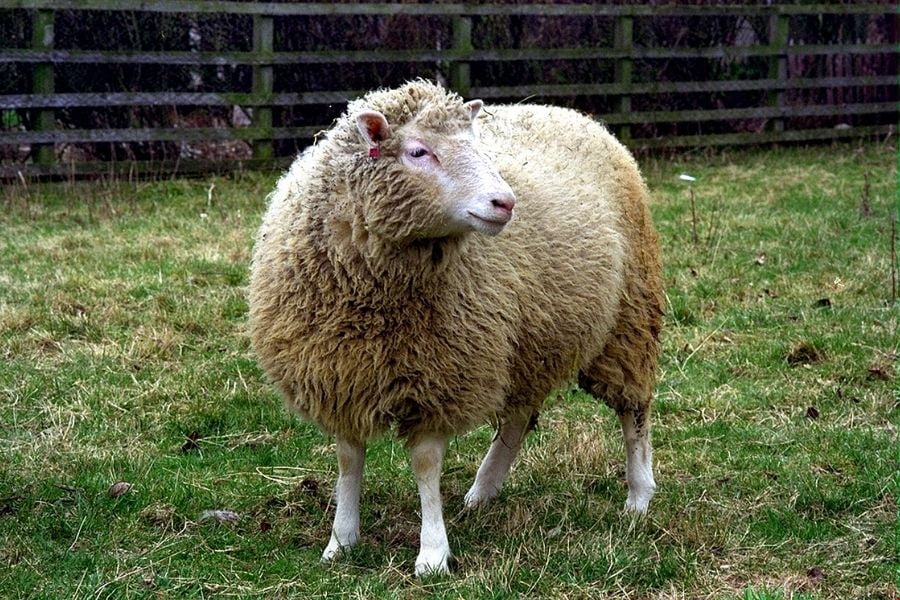

It is known that the first cloned animal was Dolly which was a sheep born in the year 1996. The news got a lot of criticism and debates about the brave new world of biotechnology. Subsequently, there have been many other clone animals including mice, cats, and monkeys. There are no human clones so far although cloned human embryos have already been manufactured. Cloning humans is a quite controversial topic with a lot of ethical issues.

Scientists say human cloning could result in a medical revolution. However, opponents assert that it can be a result of the equivalent of cannibalism.
After 3 years and many clones later, scientific research has marched ahead but the opposition has not been dropped. Cloned human embryos have already been made in the laboratory in the US, but a decision on the cloning of human embryos in the UK should be allowed in limited circumstances has been postponed.
Scientists argue that a medical revolution could result from the research, with a wide range of diseases finding cures. If it becomes widespread and successful, the technology will have found a huge international business. The opponents are of the opinion that the use of cloned human embryos to provide transplant tissue equals cannibalism.
Lots of questions and doubts might arise such as if you were ill, would you accept a transplant of perfectly-matched cells created using cloned human embryos?
Do you think that there should be a limit to how far scientists should probe the secrets of life in the quest of treating human diseases?
Conclusion
Making a clone of a human embryo is the most controversial sort of cloning now. Therapeutic cloning, as stated above; its purpose is to create human embryos for research.
Many people have opposed this type of cloning because human embryos are quite destroyed during experiments.







