Hypothyroidism and PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome) are the two most common endocrine disorders. Many of the patients are not aware, but they are closely linked to each other. Although, they are completely different disorders. They share some common symptoms but their causation is different.
There are some similarities of which we should take care of for accurate diagnosis of PCOS and hypothyroidism. Before understanding the link between hypothyroidism and PCOS, Let’s learn some basic information about hypothyroidism and PCOS.
Hypothyroidism
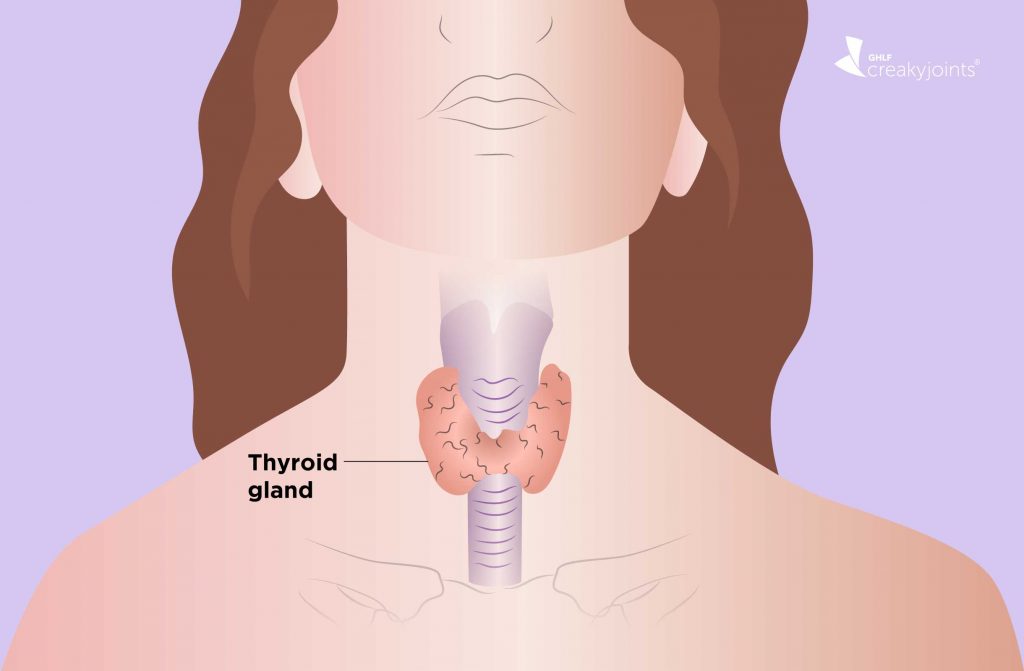
hypothyroidism is a thyroid gland disorder. The level of the prolactin and TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) is higher as compared to the normal person without hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism is commonest in hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism can be diagnosed by a blood test that is by checking the level of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) in the blood. Some of the common symptoms of hypothyroidism are weight gain, slow metabolism, hair loss, irregular period, irritability, memory loss, etc.
PCOS

PCOS is a polycystic ovarian syndrome. There is no such pathological causation found in this syndrome. The androgen hormone that is a male hormone is higher in level in the women with PCOS. Polycystic ovaries mean there is a fluid sac in ovaries. This increases the size and volume of the ovaries. PCOS can be diagnosed with ultrasound technology. Some symptoms of PCOS are weight gain, irregular period, hair loss, facial hairs, acne, etc.
To understand the relation of the link between hypothyroidism and PCOS first we should know the answer of the two questions 1. What happens to ovaries in hypothyroidism?
What happens to ovaries in hypothyroidism?

Hypothyroidism also shows the changes in the morphology of ovaries. That is polycystic ovaries are also found in hypothyroidism. There are some pathophysiological reasons behind the polycystic ovaries in hypothyroidism. Higher levels of TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone) and TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) leads to increased levels of prolactin hormone in hypothyroidism patients.
A high level of prolactin hormone leads to polycystic ovaries. Due to polycystic ovaries, ovulation is prevented. That is why there is an irregular menstrual cycle in hypothyroidism.
What happens to thyroid in polycystic ovarian disease?

Not as the previous question here is the possibility of changes in thyroid due to PCOS is less. LDLC (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) is higher which leads to hypothyroidism in PCOS conditions. Another reason is the increase in BMI (body mass index) or weight gain because of PCOS can lead to thyroid problems.
You see there are many similarities and common symptoms between hypothyroidism and PCOS. Obesity, irregular period, polycystic ovaries, high level of LH (Luteinizing hormone) and FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone )hormones, an increase of insulin resistance, high leptin, and deranged autoimmunity are present in the disorders. Because of irregular periods and polycystic ovaries, there is infertility in the patients. Both hypothyroidism and PCOS are lifestyle disorders.
The main baseline cause of hypothyroidism and PCOS is the woman lives a sedentary lifestyle. Sedentary lifestyle includes eating unhealthy food, not moving much, being in one place for many hours, intake of sugar is high, the sleeping pattern is disturbed. Depression and stress are also one kind of position that can trigger hypothyroidism and PCOS. One can also have hypothyroidism and PCOS because of genetic reasons.
Obesity

In hypothyroidism, due to higher levels of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) that increases the BMI (body mass index) of people. Weight gain can also because of the high level of leptin hormone.
In PCOS, weight gain is because of a baseline higher level of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) and leptin hormone.
Poly cystic ovary
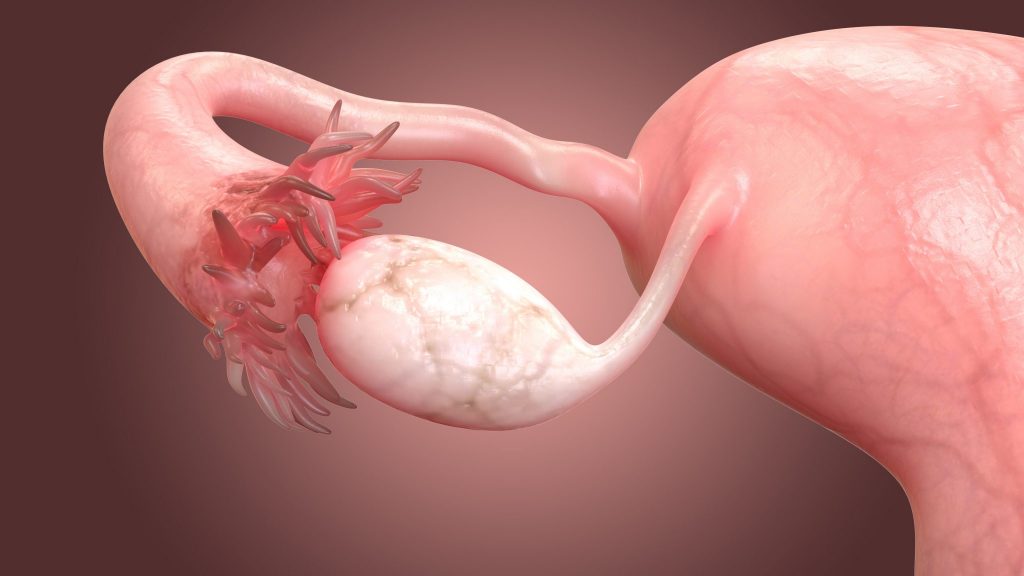
In hypothyroidism, polycystic ovaries are present because of high levels of prolactin hormone.
In PCOS, the egg or the follicle doesn’t grow or mature because of the high level of androgen hormone that is a male hormone that leads to polycystic ovaries.
Irregular period

The reason is the same as for the polycystic ovaries. In Hypothyroidism, the high level of prolactin hormone prevents ovulation.
In PCOS, ovulation doesn’t take place due to the high level of androgen hormone that is a male hormone.
Conclusion
We can see a direct link between hypothyroidism and PCOS but the pathophysiological relationship remains unknown. There is no such evidence of a relationship or the link between PCOS and hypothyroidism pathologically. There is no literature supporting the relation between hypothyroidism and PCOS. Hypothyroidism and PCOS have a complex relationship but with the proper diagnosis and knowledge, these disorders can be treated.







