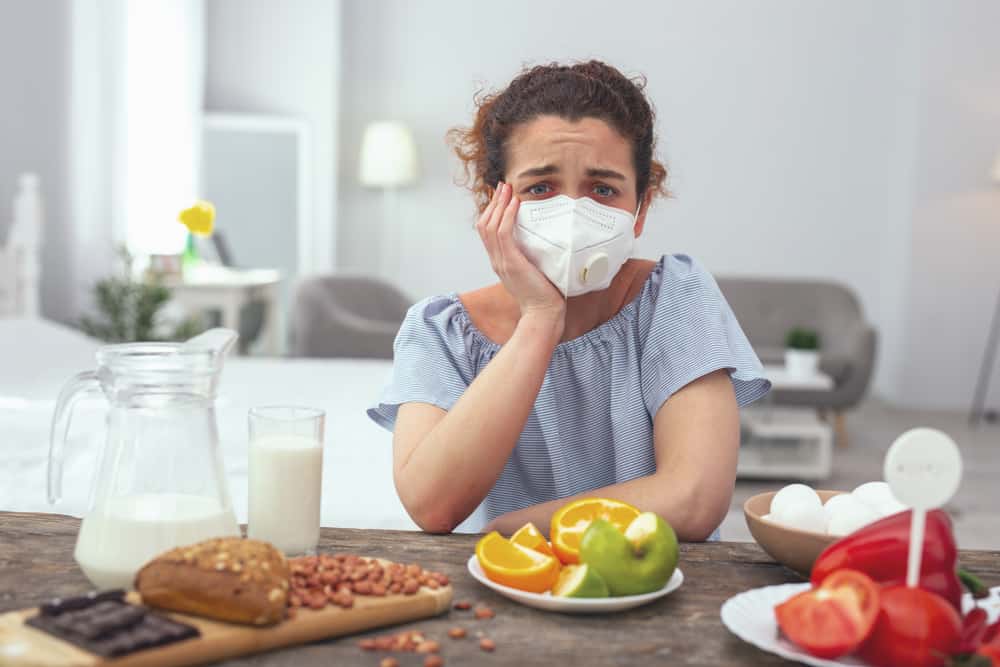
Food allergies are becoming more and more common these days.
The body’s immune system keeps you healthy by fighting off the infections and other dangers for good health. An “allergy” is said to as “a hypersensitivity reaction which is initiated or provoked by strongly suspected immunologic mechanisms”.
Food allergy is that abnormal response to a food which is often triggered by your body’s immune system. It occurs when your body’s natural defence mechanism overreact to exposure to a particular substance and sending out chemicals continuously to fight against it. According to the Centre’s for Disease Control and Prevention, food allergies are estimated to affect 4% – 6% of children and 4% of adults.
A major condition of a food allergy
When you have a food allergy, your immune system mistakenly identifies a specific food as harmful sometimes. In response, your immune system triggers cells to release an antibody known as immunoglobulin E to neutralize the allergy-causing food.
Just because an initial reaction causes a few problems doesn’t mean that all reactions will be similar. ALWAYS REMEMBER a food that triggered only mild symptoms on one occasion may cause more severe symptoms LATER.
Anaphylaxis:
- The most severe allergic reaction is anaphylaxis which is said to as a life-threatening whole-body allergic reaction that can impair your breathing, cause a drop in your blood pressure and affect your heart rate.
- Even that Anaphylaxis can come on within minutes of exposure to the trigger food. It can even be fatal and hence must be treated promptly

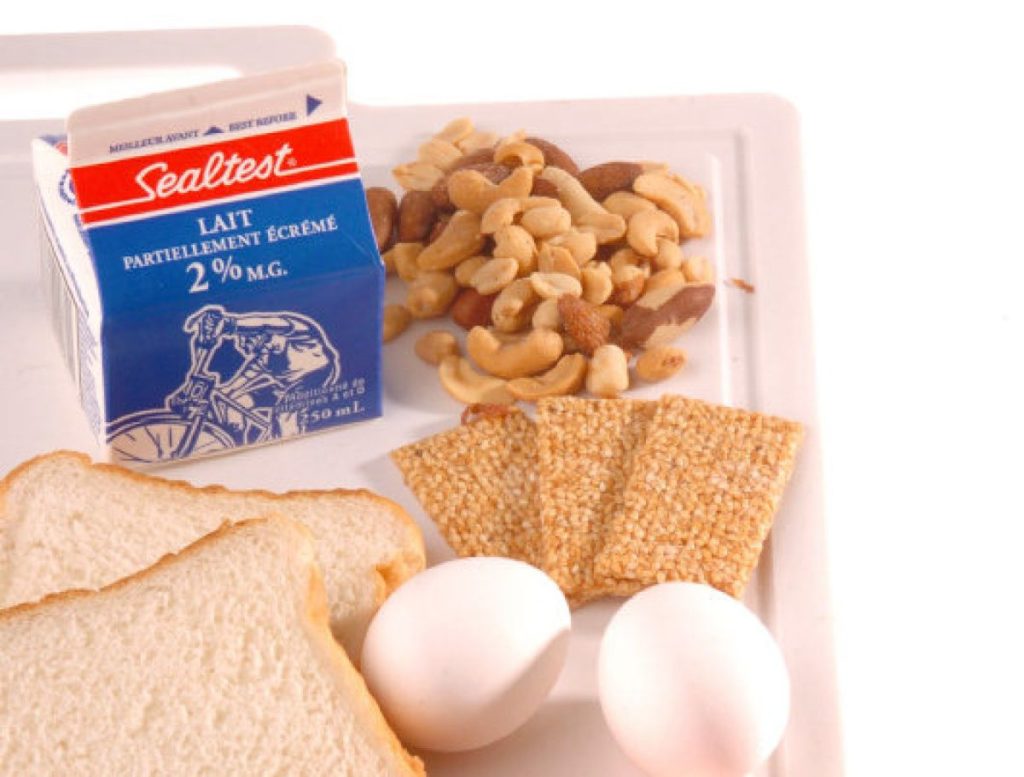
Food allergens that trigger the symptoms via foods are as follows:
In the case of children, food allergies are triggered by proteins mainly in:
- Peanuts
- Eggs
- Milk
- Wheat
- Tree nuts
- Soy

In adults, the majority of food allergies are triggered by proteins in:
- Shellfish, such as shrimp, lobster and crab
- Peanuts
- walnuts
- pecans
- Fruit and vegetable pollen (oral allergy syndrome)
Other forms of allergy:
Cross-reactive: People who are allergic to a type of food may potentially have a reaction to its related foods. For example, a person allergic to one walnut may be cross-reactive to others. Those who are allergic to shrimp can react to crab and lobster.

Pollen-food allergy syndrome:
It is known as oral allergy syndrome which affects many people who have hay fever. In this condition, certain fresh fruits, nuts, spices and veggies can trigger an allergic reaction.

Exercise-induced food allergy:
There are certain foods that may cause to feel itchy and lightheaded soon after starting to exercise. Serious cases may even involve hives or even anaphylaxis. It is important to identify the foods which cause itching and these should not be consumed before exercise.


Most common foods that account for allergies:
The types of food account for about 90 % of all reactions:
- Fish
- Tree nuts
- Eggs
- Milk
- Shellfish
- Wheat
- Soy
- Peanuts
- Some seeds like sesame and mustard seeds also are common food allergy triggers
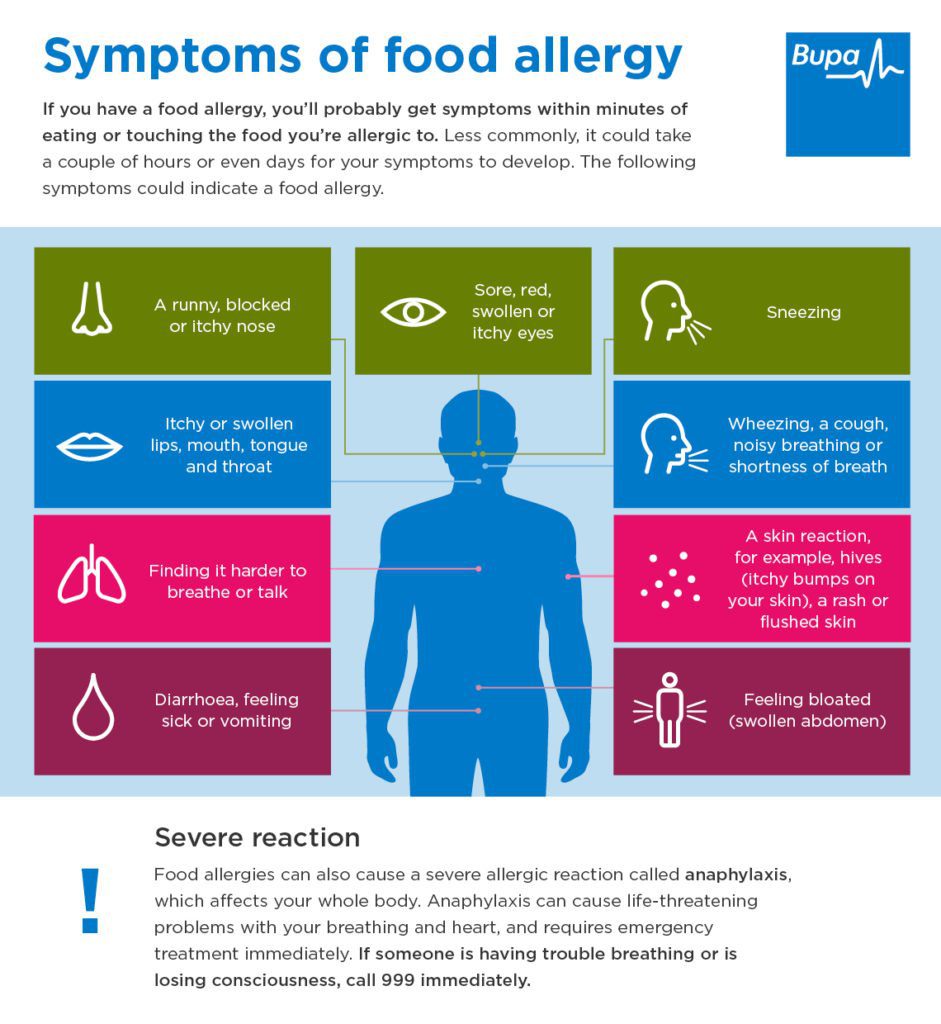
Symptoms of food allergies:
Symptoms affect the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), and the respiratory tract causing symptoms like
- Vomiting
- stomach cramps
- Shortness of breath
- Repetitive cough
- Shock or circulatory collapse
- Wheezing
- Pale or blue colouring of the skin
- Dizziness
- Swollen tongue , affecting the ability to talk or breathe
- Weak pulse
- Hives
- hoarse throat
- trouble swallowing
Common conditions that lead to symptoms:
There are certain conditions that can cause signs and symptoms which are mistaken for a food allergy include:
- Food poisoning – It can mimic an allergic reaction. For example Bacteria in tuna that has been spoiled already can make a toxin that triggers some harmful reactions.
- Lactose intolerance– Absence of an enzyme needed to fully digest a food. Nil or low quantities of the enzyme lactase reduce your ability to digest lactose, the main sugar in milk products. Lactose intolerance can cause bloating, cramping, diarrhoea etc
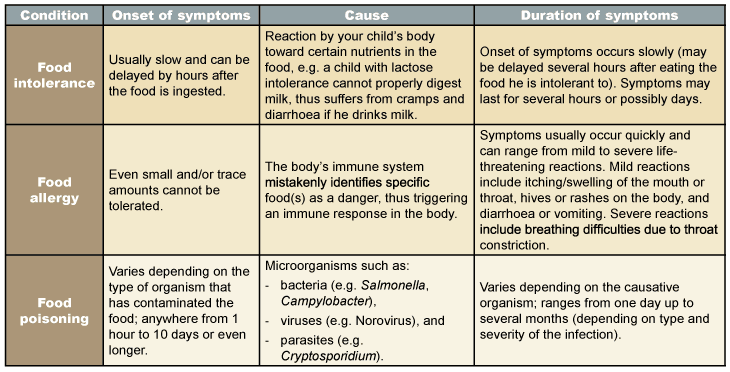
- Histamine toxicity-Fishes such as tuna or mackerel, that have not been refrigerated properly and contain high amounts of bacteria and higher levels of histamine that trigger symptoms similar to those of food allergy.
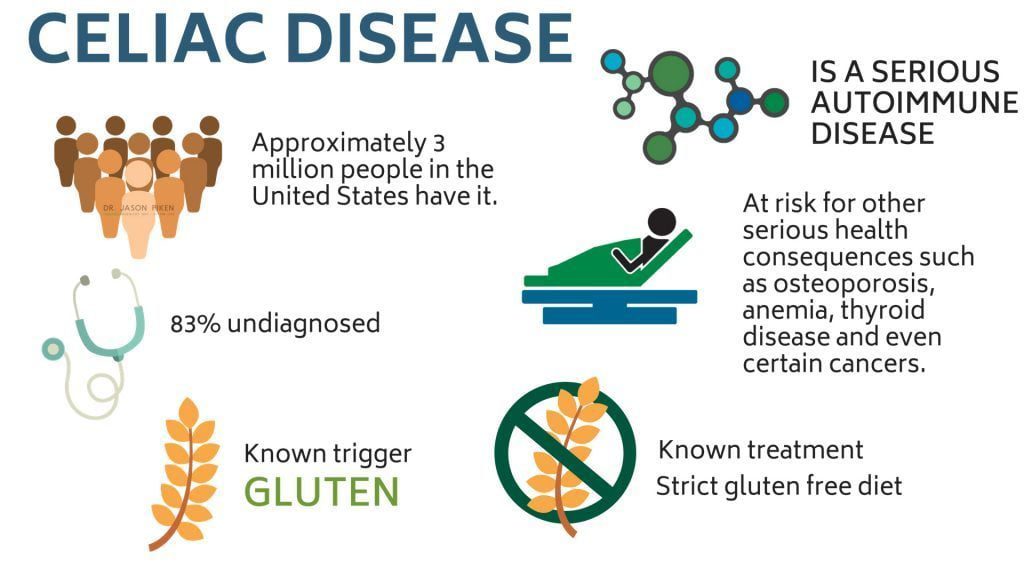
- Celiac disease. It does not result in anaphylaxis. Like a food allergy, it does cause an immune system response, it’s a unique reaction that’s more complex than a simple food allergy.
- Sensitivity to food additives. food additives such as sulphites which are commonly used to preserve dried fruit, canned goods and wine can cause asthma attacks in sensitive people.

What you can do if you have allergy symptoms right after eating any particular FOOD?
- Physician/allergist:
- You must See a doctor/allergist if you have food allergy symptoms shortly after eating.
- Food allergy reactions are unpredictable. It keeps on changing time to time.
- You should be watchful and prepared to give medication from the moment you know or suspect you or a loved one has ingested an allergen.

- Antihistamines
- Mild to moderate symptoms (e.g., itching, sneezing, rashes) can be treated with antihistamines. Severe symptoms (like trouble breathing or swallowing) can be signs of the life-threatening condition anaphylaxis. This requires immediate treatment.
- Always Work with the doctor or physician to create an individualized written plan so you and others will know what to do in case of an emergency situation

Food Allergies can be Serious?
Food allergy occurs in response to any food, and some people are allergic to even more than one food. Always take food allergies seriously. Food allergy reactions may vary from mild to severe reaction depends on the person. Mild food allergy reactions include few hives or minor abdominal pain, though some food allergy reactions progress to anaphylaxis with low blood pressure and even you can suffer a loss of consciousness.

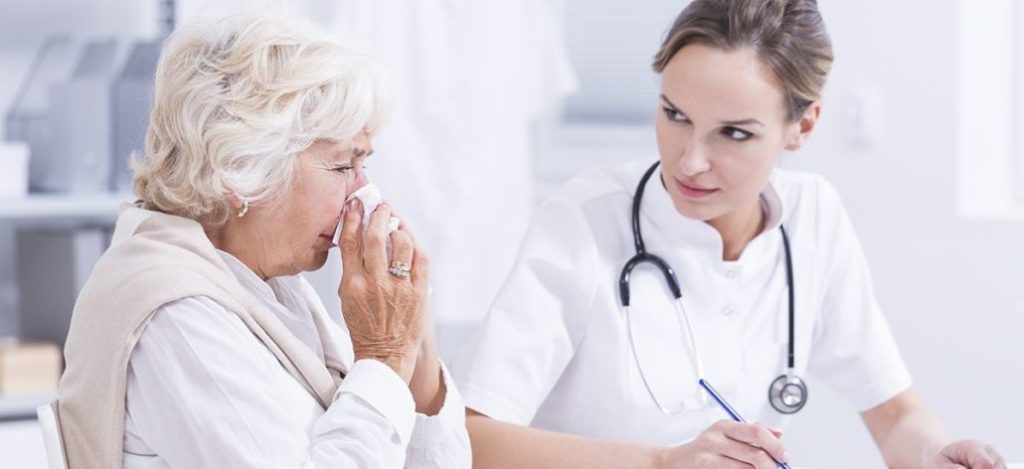
Diagnosing Food Allergies:
- every time the trigger food is eaten food allergy occurs. Symptoms can vary and you may not always experience the same symptoms during every reaction.
- It is quite impossible to say how severe the next reaction might be, and all patients with food allergies must be counselled properly about the risk of life-threatening anaphylaxis that is treated with epinephrine hormone.

- Allergists ask detailed questions about your medical history and your symptoms to make a diagnosis, the questions are as follows:
- What and how much you ate?
- What symptoms you experienced and how long they lasted.?
- How long it took for symptoms to develop?

- Then allergist will ask you to go for skin tests and/or blood tests, which indicate whether food-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies are present in your body:
- Skin-prick tests – provides results in 20 minutes. Here a liquid containing food allergen is placed on the skin of your arm or back and then your skin is pricked with a sterile probe, allowing the liquid to go under the skin. The test is considered as a positive one if a wheal (resembling the bump from a mosquito bite) develops at the site where the suspected allergen was injected. As a control, you’ll also get a skin prick with a liquid that doesn’t contain the allergen; this should not provoke a reaction.

- Blood tests-are a bit less accurate than skin tests, which will measure the amount of IgE antibody to the specific food(s) those are being tested. Results are typically available in about a week. Your allergist will utilize the results of these tests for diagnosis.
- The positive result does not confirm indicate that there is an allergy, though a negative result is useful in ruling one out.

- Oral food challenge -An allergist will recommend an oral food challenge, which is considered an accurate way. An oral food challenge is conducted under strict medical supervision. Here the patient is fed tiny amounts of the trigger food in increasing doses over a period of time, followed by a few hours of observation to see if a reaction occurs. This test is helpful when the patient history is unclear or if the skin or blood tests results are not proper.
Treatment:
One important way to avoid an allergic reaction is to avoid the foods that cause symptoms. However, despite your best efforts, you can come into contact with a food that causes a reaction.
- For a minor allergic reaction, over-the-counter drugs or prescribed medications can be taken after you are exposed to an allergy-causing food to help relieve itching or hives.

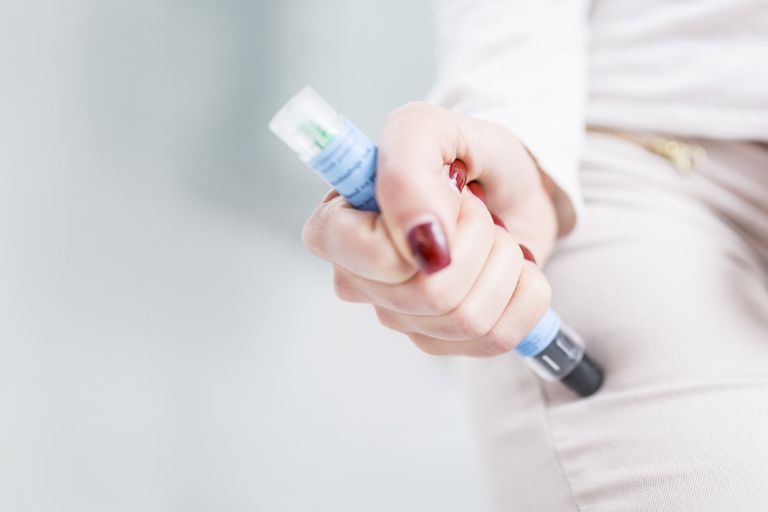
- For a severe allergic reaction, you may need an emergency injection of epinephrine and a definite visit to the hospital. Any kind of injection should be taken under medical supervision.
- Even it has been studied and observed that many with food allergies carry an epinephrine autoinjector (Example Adrenaclick, EpiPen). This device comprising of the syringe and a concealed needle that injects a single dose of medication when pressed against your thigh.
- But always be sure you know how to use the autoinjector. Also, make sure the people closest to you know how to administer the drug.
- Always make sure to replace expired epinephrine.

Some more treatments or therapy still under study are:
- For a severe allergic reaction, you may need an emergency injection of epinephrine and a definite visit to the hospital. Any kind of injection should be taken under medical supervision.
- Even it has been studied and observed that many with food allergies carry an epinephrine autoinjector (Example Adrenaclick, EpiPen). This device comprising of the syringe and a concealed needle that injects a single dose of medication when pressed against your thigh.
- But always be sure you know how to use the autoinjector. Also, make sure the people closest to you know how to administer the drug.
- Always make sure to replace expired epinephrine

- Oral immunotherapy– Researchers have been studying the use of oral immunotherapy for the treatment for food allergy. Here small doses of the food you’re allergic to are swallowed or placed under your tongue. The dose of allergy-triggering food is gradually increased. But here more researches are needed to confirm. You should learn that oral immunotherapy needs a time commitment to be successful. It starts with an initial administering of incremental doses of very dilute allergen preparations to the patient over a period of 6 hours and this prepares your immune system to start accepting doses of the dilute preparation at home. Doses are then gradually increased under medical supervision in every 1-2 weeks, over a period of 6-12 months. Once a patient successfully reaches his/her “maintenance dose”, the fear of a reaction from cross-contamination or accidental ingestion is essentially eliminated.

Lifestyle and home remedies that you can embrace:
- One of the keys to preventing an allergic reaction is to completely avoid triggering food.Always read food labels to make sure they don’t contain an ALLERGIC ingredient. Read food labels carefully to avoid the most common sources of food allergens: milk, eggs, tree nuts, fish peanuts, shellfish, soy and wheat.

- At restaurants and social gatherings, you might eat a food you’re allergic to. Many don’t understand the effect of an allergic food reaction and may not realize that even a tiny amount of food can cause a major reaction.
- Involve caregivers. If your child has a food allergy, enlist the help of relatives, baby sitters and other caregivers. Make sure that they realize how important it is for your child to avoid the symptoms of triggering food.







