Cervix is the narrow entrance part of the uterus or referred to as the neck of the womb. When uncontrolled growth of cells occurs in the cervix, it spreads to nearby tissues, organs alarming cancer. Cervical cancer is the most prevailing cancer in women after breast cancer and is mainly seen in underdeveloped regions. We will learn about cervical cancer and its causative factors, symptoms, and prevention and treatment plans.
Risk Factors Of Cervical Cancer
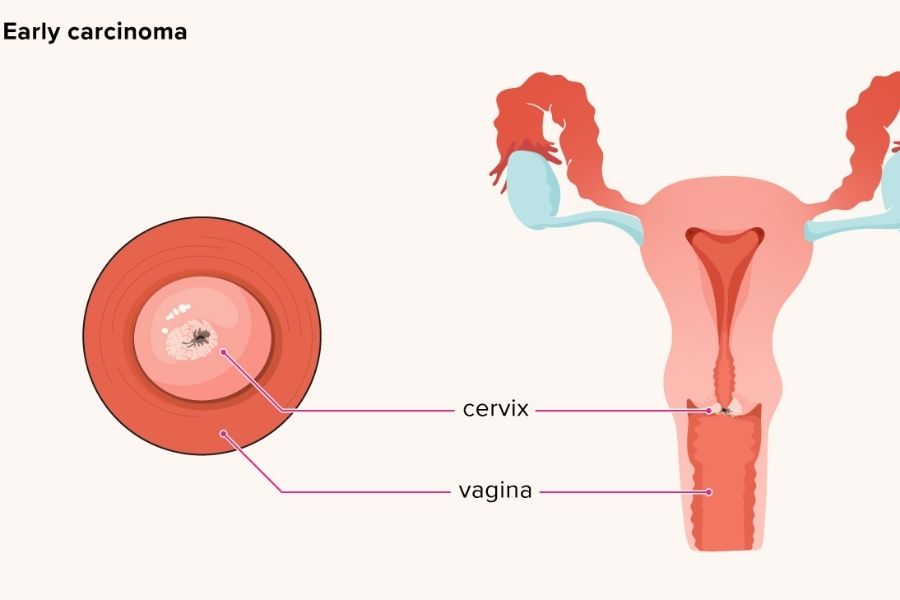
1. HPV
Human Papilloma Virus is the prominent cause of cervical cancer transmitted sexually. About 150 types of HPV exist, and 15 types can cause cancer. HPV contains the genetic material which enters into the cervix and disturbs normal cellular function—the results in uncontrolled cell growth, which turns into a cancerous tumor.
2. Birth Control Pills
Various studies indicated that excessive use of contraceptive pills raises the chances of cervical cancer.
3. Smoking
Smoking is injurious to health whether active or passive therefore enhances the cancer risk. Researchers suggest that cigarette smoke damages the DNA of the cervix which contributes to cancer growth.
4. Early Pregnancy
When women had conceived at their early age such as 17 have high possibilities of cancer compared to women 25 or older.
5. Heredity
Cancer can be passed down among family members. If your mother had cancer, then you might undergo the same in the future.
6. Multiple Pregnancies
Yet not clear but said if women have two or more children has probably the high chances of cancer.
7. Chlamydia Infection
Women who get infected in the past with chlamydia have a high risk of cancer. Other sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea, syphilis also could be the reason.
8. Dangerous Chemicals At Work
Tetrachloroethylene is the most used chemical in dry cleaning. If you expose to this, you may face the risk of cancer.
Warming Signs Of Cervical Cancer

Most of the cancers do not show noticeable symptoms at the early stages. Symptoms appear only after they spread to the nearby body parts—tissues, lymph nodes, etc.
Common symptoms when a tumor develops in the cervix are below:
- Unusual heavy bleeding during menstruation
- Vaginal watery discharge with a foul odor
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Pain and discomfort during or after intercourse
When cervical cancer spreads to the pelvic part or elsewhere in the body, the following symptoms are observed:
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Back pain, leg pain, or swelling
- Urine or feces discharge from the vagina
- Bone fractures
The infection also could be the causative factor of the above symptoms. Although it experiences any of the above symptoms, consult the physician right away to avoid the danger of advanced cancer.
Screening Tests For Cervical Cancer

It can be scary if you get to know you have cancer. But how do I know if I have cervical cancer? Following are the screening tests below to detect precancerous cells which may develop into cancer cells.
- Pap test and HPV DNA test: Pap test is painless to detect any abnormalities of the cervix cells, and women between the age of 21 to 60 should go for it. The HPV DNA test is done along with Pap to examine the cervix cells are infected with HPV or not as this is the most prominent cause of cancer.
If these tests reveal any positive results, then the doctor would suggest you for further following screenings:
- Colonoscopy: This is the visual examination of the cervix, vagina, and vulva using a coloscope.
- Punch Biopsy: It is done using a sharp tool to scrap the section of cervical tissue.
- Cone biopsy: The doctor takes the small cone-shaped section of the abnormal tissue from the cervix or any suspicious area for cancer.
If above both these biopsy worrisome, the doctor would recommend the following:
- Electrical wire loop: Local anesthesia is given as using a thin low voltage electrical wire to get the sample.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves create to visualize the image of the affected area.
- MRI and CT Scan
- Blood tests: It is done to identify any kidney or liver problems.
Treatment For Cervical Cancer
If you are diagnosed with cancer, then it is treatable if caught at an early stage. But the treatment depends upon the cancer stage. There are various treatment plans to relieve the symptoms and live longer. But treatment is wholly based upon the cancer stage, type of cervical cancer. The doctor also considers the age criteria and maintains the ability to get pregnant in the future. Following are the treatment options:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation
- Surgery
- Targeted Therapy
1. Early Stage Treatment (Surgery)
Surgery is the main treatment when cancer has not spread. Sometimes, radiation therapy is also given to prevent its recurrence. Also, chemotherapy is done before the operation to shrink the tumor and to make the surgery easier.
2. Advanced Stage Options
1. Radiation Therapy

When the cancer is extended towards other body parts, then surgery is not the only preference. The treatment involves the use of high beam energy X-rays to destroy the cancerous cells.
You can get the radiation in two ways –
- Brachytherapy: The procedure is done by placing a small device near the cervix part at the early stage.
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT): EBRT is done along with Brachytherapy for advanced cancer. The radiation is given from a machine outside the body. When radiation is targeted for the pelvic area, below the symptoms are observed until the treatment is over.
A patient may experience the following symptoms:
- The most common nausea and vomiting
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Early menopause
- Narrowing of vagine
- Bladder irriatation
- Diarrhoea
- Fatigue
- Frequent and difficulty while urination
- Skin colour changes
- Swollen legs
2. Chemotherapy

The treatment involves using drugs to kill the cancer cells, and you can also get it through IV. Doctors generally give the chemo and radiation altogether for better improvement. But you will find similar side effects just as Radiation therapy.
3. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs, such as Avastin, to destruct the cancer cells but spares the healthy cells. It works to prevent new blood vessel formation required for tumor growth nourishment. Doctors usually combine targeted therapy with chemo, and the side effects are high BP, blood clotting, appetite loss.
4. Immunotherapy

Immunotherapy is targeted for cancer recurrence after chemotherapy. Immunotherapy uses the patient’s own immune system to destroy the cancer cells.
Preventive Tips For Cervical Cancer
- Regular cervical screening: the test doesn’t detect cancer but indicate the changes of the cells
- HPV Vaccine: If the female keep up with the HPV program, then chances of cancer are decreased.
- Less likely to infect with HPV as fewer sexual partners
- Stop smoking
- Keep the healthy weight
- Eat healthy food
- Avoid excessive use of birth control pills







